Skin Cancer Treatment in Toms River & Manasquan, NJ
How common is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States.Current estimates are that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. It is estimated that nearly 9,500 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with skin cancer every day. Researchers estimate that 5.4 million cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, were diagnosed in 3.3 million 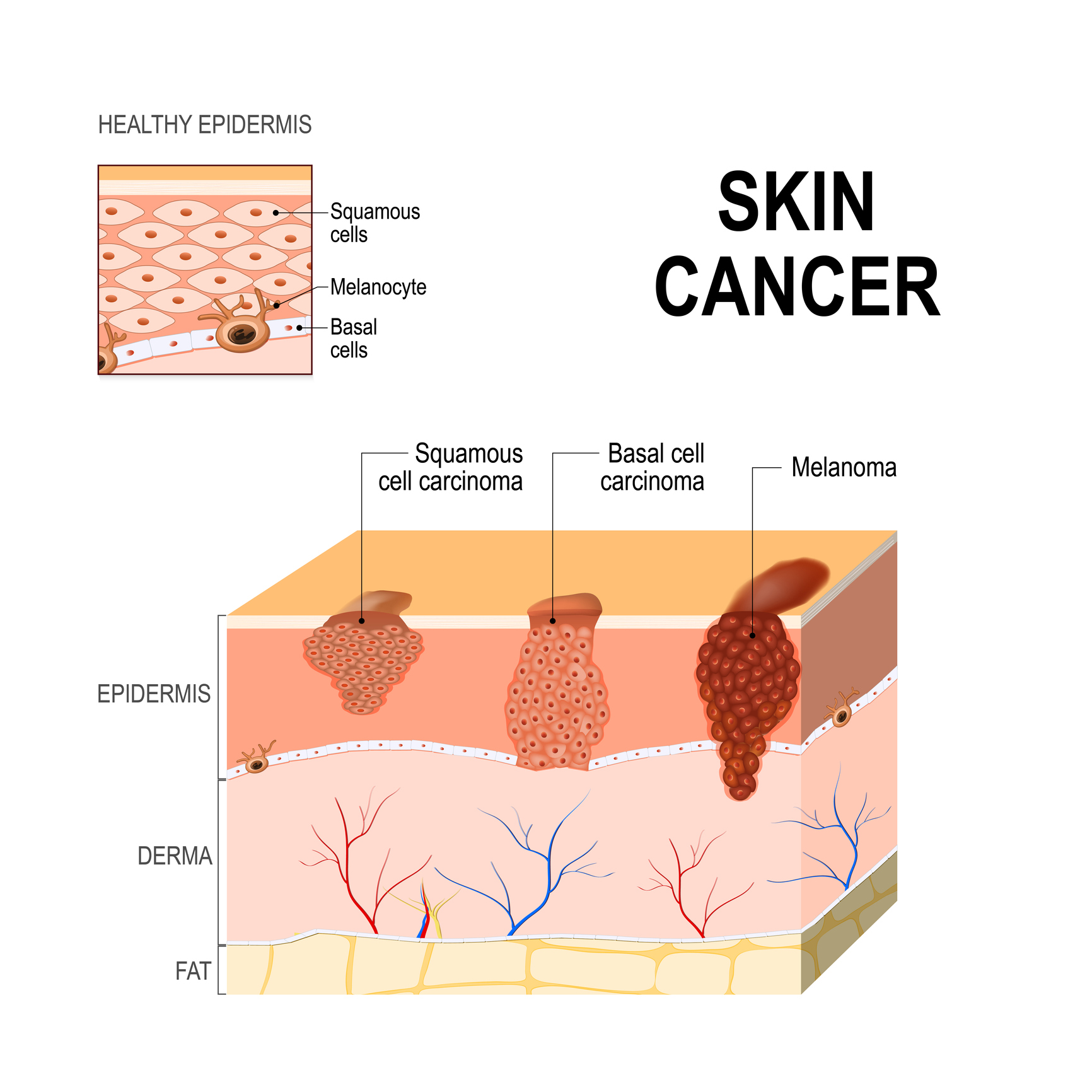
Who Is Most At Risk For Developing Skin Cancer?
Caucasians and men older than 50 have a higher risk of developing melanoma than the general population. The incidence in men ages 80 and older is three times higher than women of the same age. The annual incidence rate of melanoma in non-Hispanic Caucasians is 26 per 100,000, compared to 5 per 100,000 in Hispanics and 1 per 100,000 in African-Americans. In people of color, melanoma is often diagnosed at later stages, when the disease is more advanced. Before age 50, melanoma incidence rates are higher in women than in men, but by age 65, rates are twice as high in men. Melanoma in Caucasian women younger than 44 has increased 6.1 percent annually, which may reflect recent trends in indoor tanning. Melanoma is the second most common form of cancer in females age 15-29. Melanoma is increasing faster in females age 15-29 than in males of the same age group.
What Are the Most Common Forms of Skin Cancer?
There are a few different types of skin cancer. The top three forms, in order, are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- Basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing form of skin cancer that is caused by excessive sun exposure. While typically not fatal, this type of skin cancer can spread to surrounding tissues.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is also caused by sun exposure. However, it can also develop on the genitals and in mucous membranes that are never exposed to sunlight. This type of skin cancer, if not treated, can invade tissues under the skin.
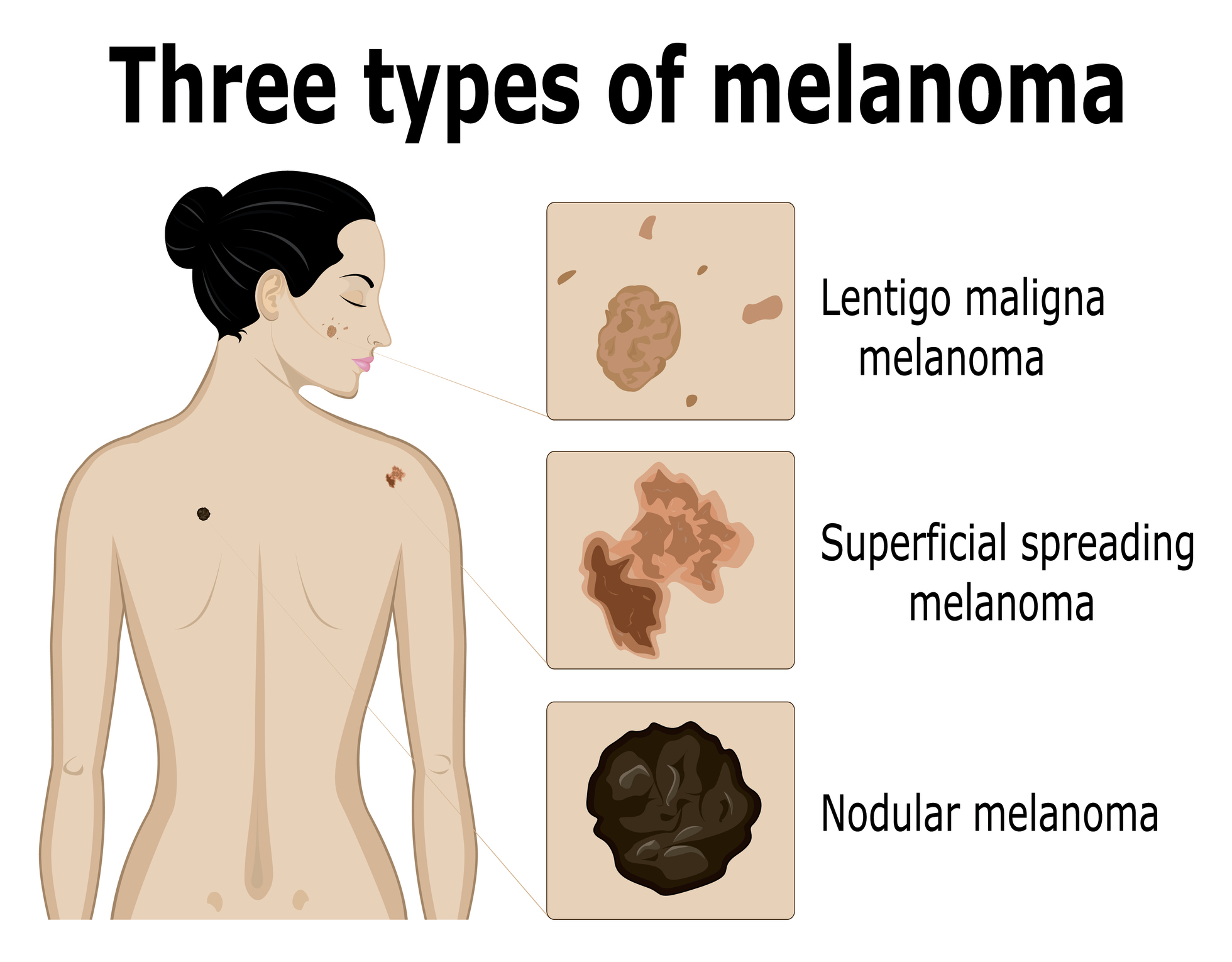
- Melanoma is the most serious of the three common forms of skin cancer. Fortunately, it is far less common than the other two. Melanoma may develop anywhere on the body and may spread to the lymph nodes or other organs and tissues.
What Are the Warning Signs?
Spots, changing moles, and patches on the skin are the most common early warning signs of abnormal cell growth. People of all ages are encouraged to check their skin monthly. This creates a familiarity that will result in the quick noticing of changes in mole shape, color, or other characteristics. The more you know your skin, the faster you may spot new growths or patches of skin that itch, bleed, or expand. If you’ve never had a skin cancer screening, we suggest that you contact a dermatologist in your area and get one scheduled. This screening can provide you with the baseline that can guide your future self-exams.
What Are the Treatments for Skin Cancer?
The most common treatment options for skin cancer include simple excision, cryosurgery, and curettage and electrodesiccation. Recently, more dermatologists have completed fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery. This micro-surgical technique is considered the gold standard because its process minimizes the removal of healthy tissue while simultaneously maximizing treatment outcomes overall. Mohs is nearly 100 percent effective at removing all cancer cells in a single procedure. It also has the least amount of scarring. Other treatments are efficient and have been proven effective but some may incur more significant scarring. A plastic surgeon may be involved in the treatment of skin cancer, performing the necessary repair to lessen visible skin cancer scars.
Can Skin Cancer be Cured?
Yes. Nearly any skin cancer can be cured if the lesion is treated early. If you notice signs of abnormal tissue anywhere on your body, it is wise to schedule a visit with a board-certified dermatologist.
How is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
A few steps may be involved in obtaining an accurate diagnosis of skin cancer. First, your doctor will perform a thorough visual examination of your skin. Some dermatologists use an instrument called a dermatoscope. This enhances the visual field with light and magnification. If the mole or spot in question looks suspicious, the doctor will likely take a biopsy. This is a small sample of the growth that may be obtained by scraping a few skin cells or using a punch biopsy that removes a small piece of tissue. The sample is examined in a lab to identify if cancer cells exist and, if so, what cells (basal cell or squamous cell) are involved.
Skin Cancer Survival rates
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas, the two most common forms of skin cancer, are highly curable if detected early and treated properly. The five-year survival rate for people whose melanoma is detected and treated before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 98 percent. Five-year survival rates for regional and distant stage melanomas are 62 percent and 18 percent, respectively.
Death Rates From Skin Cancer
The vast majority of skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. On average, one American dies from melanoma every hour. In 2017, it is estimated that 9,730 deaths will be attributed to melanoma — 6,380 men and 3,350 women. According to a recent study, men diagnosed with melanoma between the ages of 15 and 39 were 55 percent more likely to die from melanoma than females diagnosed with melanoma in the same age group. An estimated 3,860 deaths from skin cancers other than melanoma and NMSC will occur in the United States in 2017. The World Health Organization estimates that more than 65,000 people a year worldwide die from melanoma.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
Exposure to natural and artificial ultraviolet light
- Avoiding this risk factor alone could prevent more than 3 million cases of skin cancer every year.
- Research indicates that UV light from the sun and tanning beds can both cause melanoma and increase the risk of a benign mole progressing to melanoma.
Increasing intermittent sun exposure in childhood and during one’s lifetime
- Even one blistering sunburn during childhood or adolescence can nearly double a person’s chance of developing melanoma.
- Experiencing five or more blistering sunburns between ages 15 and 20 increases one’s melanoma risk by 80 percent and nonmelanoma skin cancer risk by 68 percent.
- In 2010, new research found that daily sunscreen use cut the incidence of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, in half.
- People older than 65 may experience melanoma more frequently because of UV exposure they’ve received over the course of their lives.
- Higher melanoma rates among men may be due in part to lower rates of sun protection.
Exposure to tanning beds, especially in women 45 and younger.
- Researchers estimate that indoor tanning may cause upwards of 400,000 cases of skin cancer in the U.S. each year
- In females 15 to 29 years old, the torso/trunk is the most common location for developing melanoma, which may be due to high-risk tanning behaviors.
- Higher melanoma rates among young females compared to young males may be due in part to widespread use of indoor tanning among females.
skin that burns easily; blond or red hair; and a history of skin cancer. 
- People with more than 50 moles, atypical moles, or large moles are at an increased risk of developing melanoma, as are those with light skin and freckles, and those with a personal or family history of melanoma.
- Melanoma survivors have an approximately nine-fold increased risk of developing another melanoma compared to the general population.
Men and women with a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer
- Women with a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer are at a higher risk of developing leukemia, breast, kidney and lung cancers, and men with a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer are at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
We are specialists at caring for skin cancer patients. We work closely with dermatologists to provide the latest in skin cancer removal and reconstruction.
Schedule a Consultation
If you are having concerns about skin cancer, scheduling a consultation with Fostermd can get you started on a preventative course of action. If you think you might have skin cancer, it is very important to take action immediately. Contact us to schedule a consultation with Fostermd by calling (732) 914-2233 for our Toms River location or our (732) 449-2099 for our Manasquan location. We serve Monmouth County, Ocean County, and surrounding areas in New Jersey.